
Dosing and administration1
The recommended dose of ASPARLAS® is 2500 IU/m2 administered as IV infusion no more than every 21 days.1
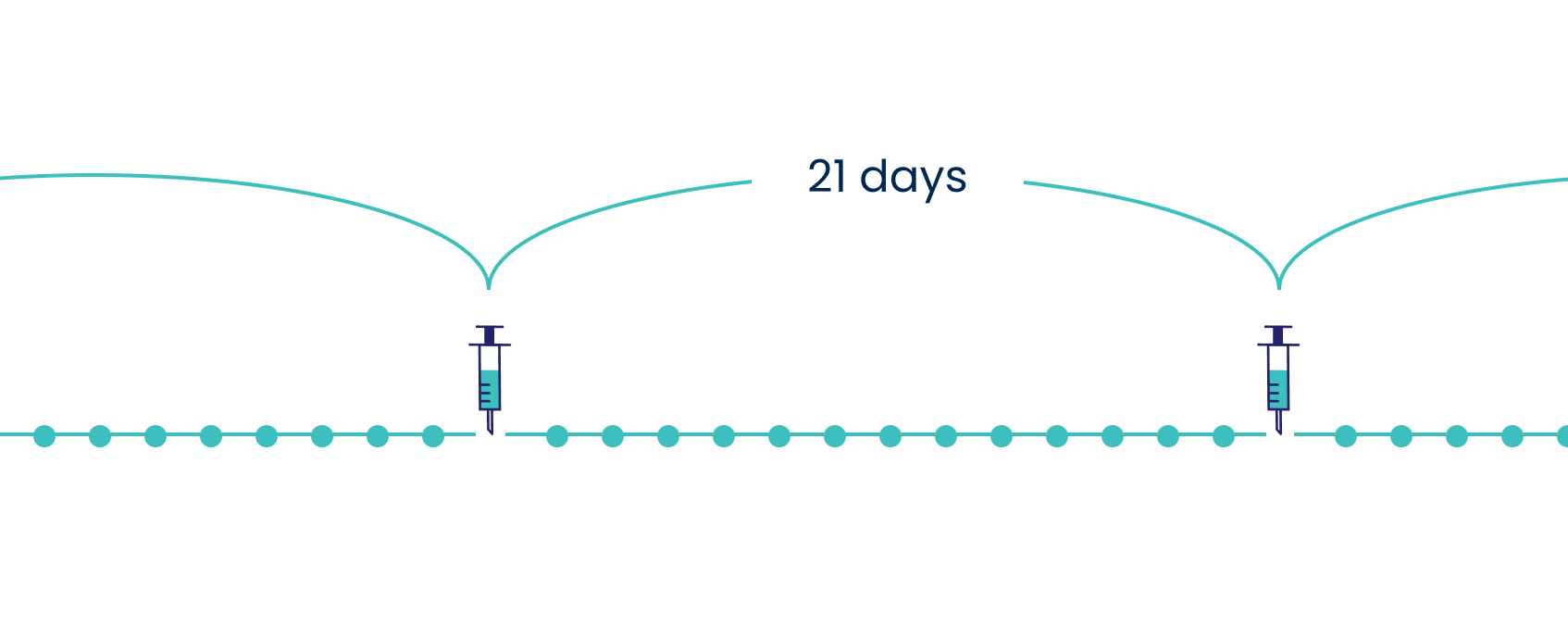
Adapted from the ASPARLAS® Product Monograph. Please see the ASPARLAS® Product Monograph for complete dosing information.
- ASPARLAS® is a preservative-free, clear and colorless solution. If particulate matter, cloudiness, or discoloration are present, discard the vial. Do not administer if ASPARLAS® has been shaken or vigorously agitated, frozen, or stored at room temperature for > 48 hours.
- Dilute ASPARLAS® solution in 100 ml of 0.9% sodium chloride or 5% dextrose solution prior to administering as an IV infusion over a period of 1-2 hours, through an infusion that is already running.
- After dilution, administer immediately into a running infusion of either 0.9% sodium chloride or 5% dextrose.
Administer over a period of 1-2 hours.
Do not infuse other drugs through the same IV line during administration.
Monitor patients at least weekly during cycles of treatment that include ASPARLAS® and through 6 weeks after the last dose of ASPARLAS®. (e.g., bilirubin, transaminases, glucose and clinical examinations until recovery from the cycle of therapy).
If an AE should occur, modify treatment according to the Product Monograph.
- ASPARLAS® is used as part of combination chemotherapy protocols with other antineoplastic agents.
- ASPARLAS® is not a bioequivalent alternative to pegaspargase.
- In a multi-agent chemotherapeutic regimen, ASPARLAS® at the same dose and frequency as pegaspargase may increase toxicities due to the longer half-life of calaspargase pegol.
Please consult the Product Monograph for the complete information on dosing and administration.
Learn more about Servier Canada’s treatment options in ALL
Consult the ASPARLAS® Product Monograph
aBFM: augmented Berlin-Frankfurt-Münster; AE: adverse event; ALL: acute lymphoblastic leukemia; ALP: alkaline phosphatase; ALT: alanine aminotransferase; aPTT: activated partial thromboplastin time; AST: aspartate aminotransferase; BFM: Berlin-Frankfurt-Munster; BSA: body surface area; CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; CTCAE: Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events; DFCI: Dana-Farber Cancer Institute; IM: intramuscular; IV: intravenous; NCCN: National Comprehensive Cancer Network®; NPAA: nadir plasma arparaginase activity; NSAA: nadir serum asparaginase activity; NSAID: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug; PD: pharmacodynamics; PK: pharmacokinetics; TDM: therapeutic drug monitoring.
* Comparative clinical significance has not been established.
† Fictitious cases. May not be representative of all patients.
‡ Clinical significance has not been established.
References:
- ASPARLAS® Product Monograph. Servier Canada.
- Data on file. Servier Canada.
- ONCASPAR® Product Monograph. Servier Canada.
- RYLAZE™ Product Monograph. Jazz Pharmaceuticals Canada Inc.
- Government of Canada. Summary Basis of Decision for Asparlas. Available at https://dhpp.hpfb-dgpsa.ca/review-documents/resource/SBD1718207489396.
- Government of Canada. ONCASPAR_CPID Redacted.
- Terwilliger T, Abdul-Hay M. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a comprehensive review and 2017 update. Blood Cancer J. 2017;7(6):e577.
- Mank V, Azhar W, Brown K. Leukocytosis. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; April 21, 2024.
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia, version 4.2023 – February 05, 2024.
- Vrooman LM et al. Efficacy and toxicity of pegaspargase and calaspargase pegol in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Results of DFCI 11-001. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(31):3496–3505.
- National Institutes of Health. National Cancer Institute. Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE): Version 4.0. Available at: https://evs.nci.nih.gov/ftp1/CTCAE/CTCAE_4.03/Archive/CTCAE_4.0_2009-05-29_QuickReference_8.5×11.pdf. Accessed December 11, 2024.
Stay Connected with Servier Canada
Stay up to date on disease information, treatment options, our products, and patient support programs.